Email turns 50: here’s its history, and how it’s changed over time

Email turns 50, and after half a century of history, it continues to play an important role in the world of contemporary communication. Despite the advent of more modern and immediate competitors like social media and messaging apps, email still has excellent performance as a channel:
- about 3.9 billion people use email;
- 99% of users check their inbox at least once a day;
- the number of active email accounts exceeds 5.6 billion;
- nearly 105 billion emails are sent every day, and
- email is users’ top tool of choice for different types of content.
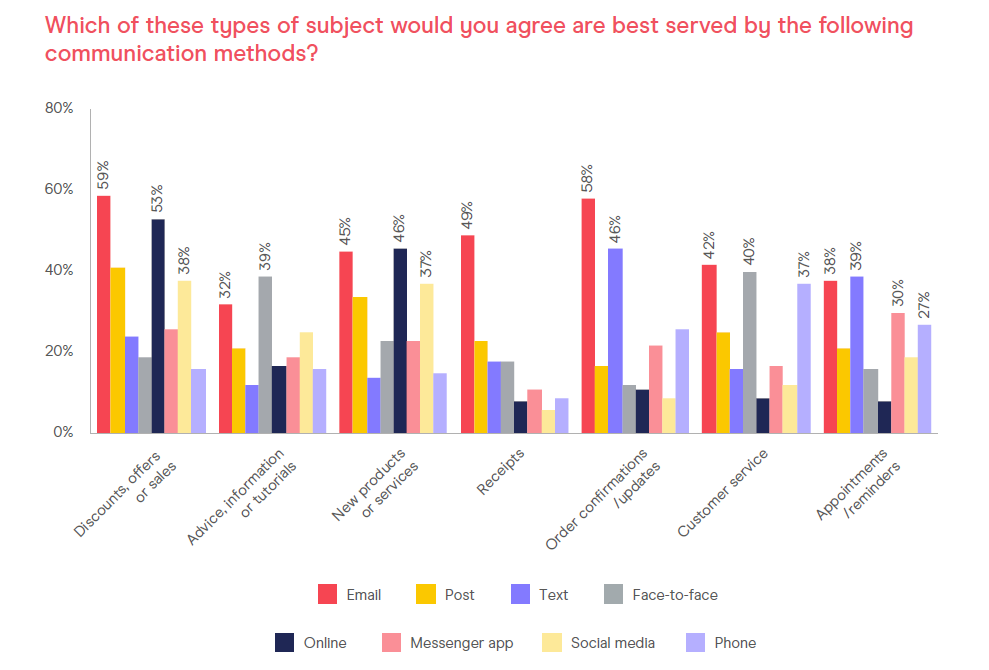
Source: Consumer Email Tracker 2021

From developing integrations to strategic support, from creating creative concepts to optimizing results.
How did email come about?
It was 1971 when an U.S. programmer, Ray Tomlinson, sent history’s first email from a Massachusetts laboratory. The email inventor was then working for Bolt Beranek and Newman (BBN). Back in 1969, this company had developed ARPANET (acronym for Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). The network was designed to connect various research organizations around the country and, today, is considered the precursor of the Internet.
SNDMSG was a primitive email program for logging into an account and messaging other users on the same computer. Tomlinson had the idea of merging that technology with the communication mechanism of the different ARPANET networks. Such an epiphany brought about the invention of the first email. Unfortunately we’ve lost its content, yet Tomlinson remembers it was a rather meaningless text, clearly for a test (“Test 123” or “QWERTYUIOP” are the most accredited hypotheses).
Tomlinson was also responsible for introducing the “@” symbol. At the time, it was used as a synonym for “at the price of”, but he used it to separate the recipient’s name from the hosting name.
Indeed, what we now regard as a revolutionary invention was by no means perceived as a turning point at the time. Tomlinson himself stated
“The awareness of how important that sending was only came on the occasion of the 25th anniversary of ARPANET. Somebody asked, ‘Where did the first email come from?’ Several people remembered that I had sent the first one and written the program, so they called me.”
The evolution of email: how it’s changed in half a century
1978: the first mass dispatch
Another important, historical achievement after the first email sent by Tomlinson had to wait until 1978. This was the channel’s first massive commercial use. The author of the first mass emailing in history was Gary Thurek. He earned a reputation as the “king of spam” for sending hundreds of ARPANET users an unsolicited email to promote a new product from the Digital Equipment Corporation. The move got him $13 million.
1981: SMTP was introduced
Jon Postel proposed a new transmission protocol to replace the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) when the ARPANET was transformed into the modern Internet network in the early 1980s. In fact, the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) was officially introduced in 1981. This protocol standardized the way in which servers send and receive messages.
1982: the term “email” was born
The expression used until then to refer to primitive e-communication was “electronic mail message”. It was shortened for the first time to “email” in 1982 and from that moment, this word became part of early adopters’ vocabulary.
1988: MSMail, the ancestor of Outlook—the first email client in history
That year, Microsoft launched MSMail a.k.a. Microsoft Email, which is the ancestor of Outlook and the first Microsoft email product. The first version was only available for Macintosh, while the PC version came later, in 1991.
That same year, moreover, the word “spam” was included in the Oxford English Dictionary, formalizing the concept of unsolicited mail.
The ’90s: the birth of the Internet started the expansion of the email channel
The last decade of the 21st century, with the introduction of the World Wide Web and the HTML language to customize messages, gave impetus to the growth of the email channel and its wide use for both private and business purposes. A series of events over these 10 years has led email to become the communication tool we know today:
- In 1991, the first email from space was sent from a Macintosh Portable of the Atlantis Shuttle crew.
- The main Yahoo! Mail, AOL, and Hotmail clients emerged between 1996 and 1998 after the forerunners, MSMail and Lotus Notes.
- In 1992, MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) made email much more flexible and put an end to text-only emails. Among the innovations introduced by MIME were the use of characters other than ASCII encoding (American Standard Code for the Exchange of Information), the aggregation of different messages together, the insertion of attachments, an unlimited and at-will length, and non-text messages.
- Also in 1992, formatting an email without knowing how to code became possible. This follows the introduction of CompuServe and a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor that allowed for customizing colors and fonts, and even fusing emoticons.
- The first version of an entirely web-based email dates back to 1993. Until then, people were compelled to use a specific software for sending and receiving emails. An idea by a CERN scholar, Philip Hallam-Baker, led to design the first implementation of a web-based email service.
1999: Permission Marketing emerged
With his book Permission Marketing, Seth Godin introduced an unconventional and revolutionary marketing technique compared to the invasive Email Marketing strategies used until that moment. The idea behind this strategy was based on sending promotional emails only to users who had previously given consent to receive that type of communication, hence the name, Permission Marketing. In fact, Godin had already intuited in 1999 that in order for an Email Marketing strategy to be effective, each campaign must have three elements:
- be made known to the user (by consent);
- be personal; and
- be relevant.
2002: email went mobile
That year, the BlackBerry 5810 was launched on the market. This was the first mobile device to welcome emails and the so-called Mobile Work Era. The possibility of checking an inbox from a phone had arrived.
2004: Gmail was born
The advent of Gmail in 2004 raised the standards of competition between various email services thanks to the introduction of previously unknown features. These included a gigabyte of storage space, the ability to initiate conversations (threads) between users and, since 2013, automatic email-sorting tabbed inbox, namely the “Main”, “Social”, “Promotions”, and “Forums” tabs.
2009–2011: email became responsive
Since its first official launch on January 9, 2007, iPhone has revolutionized the world of modern communication. It made the smartphone an indispensable technological object, used today by around 3.6 billion people. The email channel had to adapt to this success and, from that moment on, mobile optimization has been a continuous challenge.
2010–2020: email got perfected and became even more personal and automatic
While the ’90s were the decade that gave impetus to the email channel, 2010 to 2020 saw a series of changes that made email messages an even more effective and customizable tool:
- In 2010, automatic emails triggered by a user action became the norm.
- In 2014, the integration of CSS and HTML introduced the possibility of creating animations and opened the door to interactive emails. That same year, the use of dynamic fields launched email personalization.
- In 2016, the use of animations and personalization strategies became increasingly widespread in companies’ email marketing campaigns.
- In 2018, Apple introduced the Dark Mode.
2018: GDPR changed the rules
Entered into force on May 25, 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), defined a unique body of rules for the processing of personal data within the European Union. It requires companies to review their way of marketing (and, therefore, also Email Marketing) and their strategies for collecting and using people’s data.
2020: a year that changed everything
2020 marked a turning point in the world of marketing and in the history of email. The pandemic has given impetus to a process of digitization that was already in the air. It transformed the use of digital strategies and channels (especially email) from an optional choice to an urgent need (as we’ve explained in this post). This anomalous year represented a further decisive step in the growth of email messages, transforming email into an indispensable and mandatory marketing tool for companies.
The future of email: what we’ve learned over 50 years of history
Beyond the events that have marked the evolution of email over these 50 years of history, here’s what we’ve learned in harnessing the full potential of this channel:
- test, test, and test again: email, its design, and its audience are constantly evolving—what worked yesterday for the context and users of the past might not work today or tomorrow. This is why techniques like A/B testing are one of the key best practices to make email truly effective.
- measure to improve: email is an extremely measurable channel, and it’s important to keep its main KPIs monitored to ensure better performance.
- relying on a professional Email Marketing platform is always the best choice: sending platforms like MailUp offer a secure infrastructure for your messages, a top sending reputation, and excellent delivery rates.
If you haven’t chosen the professional sending platform to rely on, then find out what you can do with MailUp! Request a free trial without obligation. Start discovering the endless advantages that the platform can offer.